Learning how to become a travel agent opens up a career full of excitement, personal growth, and financial opportunity. Whether you enjoy planning itineraries, helping people find the best deals, or offering customer service in a fast-moving industry, this path offers flexibility and reward. Today, many people look for structured ways to work in the travel industry, and knowing the right steps makes a real difference.
This blog focuses solely on how to become a travel agent. It covers everything from understanding job roles to certifications, business models, tools, income sources, and real-time challenges.
Who are Travel Agents?
Travel agents are professionals who assist individuals and businesses in planning and arranging travel services. They coordinate various aspects of travel, including flight bookings, hotel reservations, transportation, and tour packages. Acting as intermediaries between travelers and service providers, they aim to simplify the travel process and ensure a smooth experience from start to finish.
With their industry knowledge and access to exclusive deals, travel agents recommend options that align with a client’s budget, destination preferences, and travel goals. They also offer guidance on essential travel requirements such as visas, documentation, and safety protocols, helping travelers make informed decisions and avoid potential issues.
Related resource: Who are Emergency Care Assistants?
How to Become a Travel Agent in 10 Steps?
Becoming a travel agent can be a rewarding path for those who enjoy planning, organizing, and helping others create memorable experiences. Here are ten important steps to consider when becoming a travel agent:
1. Understand What a Travel Agent Actually Does
Before you begin, it’s important to understand the responsibilities involved. Travel agents help clients plan trips, book travel services (flights, hotels, cruises, etc.), and provide expert advice on destinations, budgets, and itineraries. This role demands strong communication skills, attention to detail, and a passion for travel.
They also handle changes or cancellations, provide travel insurance guidance, offer 24/7 support in some cases, stay updated with travel policies and restrictions, and so on.
Knowing what’s expected of you sets the right foundation before moving forward.
2. Choose Your Travel Niche
The travel industry is broad. Picking a niche helps you position yourself as an expert and attract the right audience. Here’re some common travel niches:
- Cruises
- Eco-tourism
- Group tours
- Luxury travel
- Corporate travel
- Solo female travel
- Destination weddings
- Disney or family vacations
If you’re not sure which niche suits you, think about your own interests or areas where you have some experience. Start narrow, you can always expand later. Once you choose a niche, it will influence your branding, marketing, and partnerships.
3. Meet the Educational Requirements (Even if Optional)
There’s no strict degree requirement to become a travel agent, but having some formal education can help you gain an edge—especially when applying to agencies or building client trust. Some helpful travel programs or certifications include:
- The Travel Institute
Offers the Certified Travel Associate (CTA) and Certified Travel Counselor (CTC) designations.
(The Travel Institute) - IATA Training
Internationally recognized certifications.
(IATA Training) - ASTA Verified Travel Advisor Program
Run by the American Society of Travel Advisors.
(ASTA Verified Travel Advisor Program)
These programs cover destination knowledge, marketing, customer service, booking tools, and industry laws—everything you’ll need to perform professionally.
4. Gain Industry Experience (Or Learn Where to Get It)
Experience makes a big difference—whether you work at an agency, join a host network, or run your own business. If you’re just starting out, consider working in:
- Travel agencies (online or local)
- Airline customer support roles
- Hotel reservation departments
- Tourism boards or tour companies
For actual job openings, platforms like Indeed, Glassdoor, or LinkedIn Jobs are a good place to start. These roles can help you understand customer expectations and industry workflows.
If you prefer freelancing, look into virtual travel assistant roles to gain practical booking and itinerary planning skills.
5. Create a Business Plan If You’re Going Independent
If you’re not joining an agency, take time to create a structured plan. This ensures you’re not just working hard—but also working smart. Your business plan should cover:
- Services offered (individual bookings, group travel, custom tours, etc.)
- Pricing and commission structure
- Target audience (families, honeymooners, business travelers)
- Startup and monthly costs (website, booking tools, marketing)
- Marketing and branding strategy
- Growth roadmap
Whether you’re starting solo or with a partner, clarity here saves time and money later.
6. Register and Legally Set Up Your Travel Business
Once your plan is ready, it’s time to make it official. Register your business name, choose your structure (sole proprietorship, LLC, etc.), and secure the necessary documentation. Here’s what this usually involves:
- Registering your business with the state
- Applying for an EIN (Employer Identification Number)
- Getting a business bank account
- Checking for local or state Seller of Travel licenses (required in California, Florida, Washington, and Hawaii)
Also, check what’s required in your country. If you’re operating internationally, be aware that top countries for setting up travel agent businesses include the United States, Canada, UK, Australia, and UAE due to stable tourism demand and business support systems.
7. Join a Host Agency (Strongly Recommended for New Agents)
A host agency provides you with access to systems, suppliers, training, and higher commission rates. This is especially helpful if you’re just starting out and want support without the cost of building everything from scratch.

Look for host agencies that offer:
- Access to Global Distribution Systems (GDS)
- Higher commission splits
- Ongoing training and mentorship
- Marketing support and branding tools
- Legal and operational assistance
For your reference, here’re two trusted host agency directories:
8. Get Your Tools Ready – From Booking Software to Branding
To work efficiently, you need the right tools. This includes booking platforms, CRM systems, invoicing tools, and your own branded website. Essentials include:
- Global Distribution System (GDS) access (e.g., Sabre, Amadeus, Galileo)
- Client Relationship Management (CRM) tool (e.g., TravelJoy, Zoho CRM)
- A website with services listed clearly, contact forms, booking inquiry forms, and testimonials or case studies
Don’t forget social media presence, an email list, and professional branding that reflects your niche and personality.
9. Build Your Client Base Through Smart Marketing
Now comes the work of reaching the right audience. Focus on creating trust and authority, especially if you’re not a well-known name yet. Some effective marketing strategies include:
- Sharing travel tips and destination ideas on Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok
- Writing blogs or newsletters to educate clients
- Asking for client reviews and referrals
- Running small ads targeting your niche
- Joining local networking events or travel expos
Start small, but stay consistent. Most travel agents build their client base through word-of-mouth, so keep your service personal and helpful.
10. Keep Learning and Stay Updated with Travel Trends
The travel industry is dynamic. Airline policies, visa rules, destination popularity, and global conditions can shift rapidly. To stay ahead:
- Subscribe to travel news platforms (Travel Weekly, Skift)
- Take ongoing certifications or refresher courses
- Join associations like ASTA, CLIA (for cruises), or IATA
- Attend webinars and FAM (familiarization) trips
Ongoing learning builds credibility and helps you give clients better, more up-to-date advice—which leads to long-term loyalty.
Becoming a travel agent takes time, effort, and strategy, but it’s completely achievable if you follow each step thoughtfully. Whether you want to join an agency or run your own travel brand, the key is to stay customer-focused, continuously educate yourself, and offer services that truly make planning a trip easier and more enjoyable for your clients.
Related resource: How to Become a Professional Plumber?
More About Travel Agents
Travel agents play a valuable role in simplifying the travel experience for individuals, families, and businesses. They use their expertise, tools, and industry connections to provide reliable travel solutions that save time, reduce stress, and often result in better travel arrangements. Whether it’s a leisure vacation or a corporate trip, travel agents help ensure the journey is planned with precision.
Key Roles of Travel Agents
- Book flights, accommodations, and ground transportation.
- Arrange travel packages, including tours and activities.
- Advise on travel documentation, entry requirements, and regulations.
- Provide cost-effective solutions through access to exclusive deals.
- Assist with itinerary changes, cancellations, or travel disruptions.
Types of Travel Agents
- Leisure Travel Agents plan holidays, honeymoons, and family vacations.
- Corporate Travel Agents handle business-related travel and manage logistics for meetings or events.
- Destination Specialists focus on specific regions or countries and offer deep knowledge of those areas.
- Luxury or Cruise Travel Agents cater to premium experiences and high-end travelers.
- Independent Agent works solo or under host agencies with flexible operations
- Niche Specialist deals with specific destinations or client types
Travel Agent Earnings: Income and Commission Structure
1. Average Travel Agent Income: The income range varies depending on whether you’re working full-time, part-time, as an employee, or independently.
| Role Type | Estimated Annual Income (USD) |
|---|---|
| Entry-level/Part-time | $20,000–$35,000 |
| Mid-level Independent Agent | $40,000–$70,000 |
| Experienced Niche Specialist | $75,000–$150,000+ |
2. Commission from Travel Suppliers: This is the most common way travel agents earn money. Suppliers like airlines, hotels, cruise lines, and tour operators pay commissions when a booking is made through an agent. Here’re typical commission ranges for a travel agent:
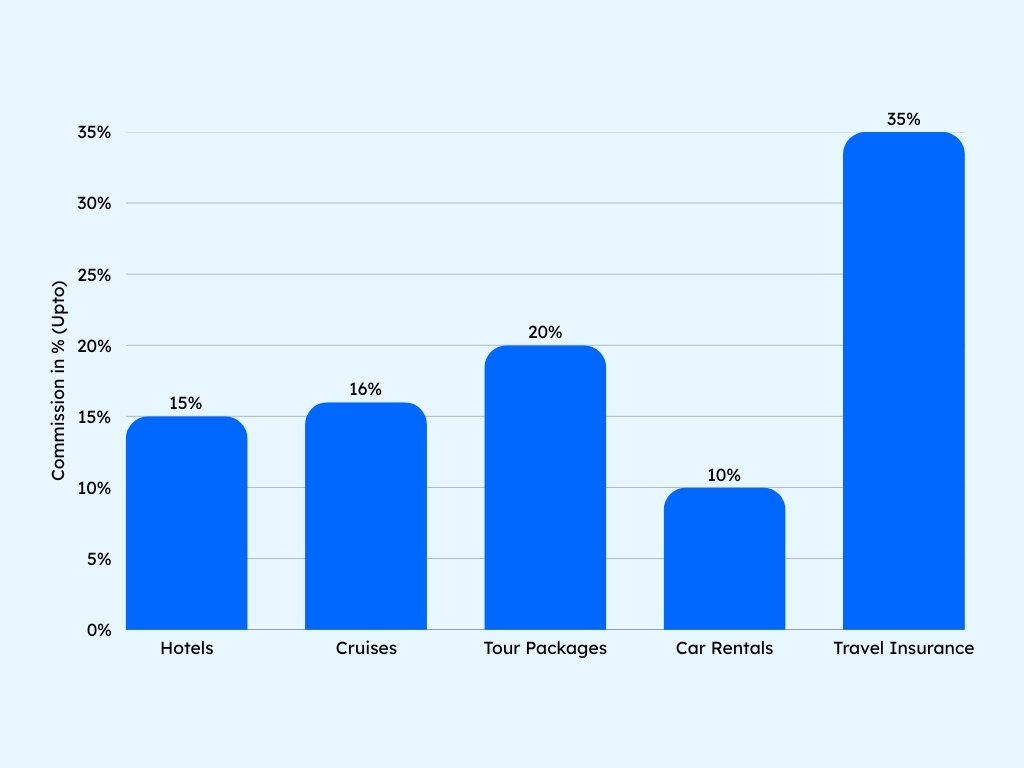
3. Service Fees: Many modern travel agents also charge clients service or planning fees to cover their time and expertise. These fees help stabilize income, especially when commission structures fluctuate. Here’re some service fee examples:
- Trip consultation: $50–$150
- Custom itinerary planning: $100–$500+
- Group or corporate travel setup: Flat or per-head fee
- Airline-only bookings: $25–$50 (since commissions on flights are usually low or non-existent)
Markups on Net Rates: Some suppliers offer net rates (wholesale prices) that allow agents to mark up the price and keep the difference. This is more common when dealing with custom travel packages, luxury travel, or private tours. For example:
- You receive a package at $1,800
- You sell it to the client at $2,100
- You retain the $300 margin
A travel agent’s income is performance-based and flexible. With the right niche, consistent client base, and strong supplier relationships, it’s possible to scale your earnings steadily. Combining commission with service fees and affiliate income can lead to a well-rounded, reliable revenue model—especially for independent agents building their brand.
Related resource: Do Real Estate Agents Make Good Money?
Final Thought
Knowing how to become a travel agent gives you a clear path to a rewarding and flexible career. It takes more than interest; it requires training, effort, and the right approach. You must stay updated with the latest tools, maintain strong networks, and deliver consistent client value. The decision to become a travel agent opens up more than just income potential. If you follow each step, keep building your knowledge, and understand the industry’s practical side, your journey as a travel agent can become successful and long-lasting. Use this guide as a roadmap and begin building your presence in the travel world today.



